Sodium calcium edetate
Sodium calcium edetate (sodium calcium EDTA), also known as edetate calcium disodium among other names, is a medication primarily used to treat lead poisoning.[1] This includes short term and long term lead poisoning.[2] For lead encephalopathy it is typically used together with dimercaprol.[2] It does not appear to be useful for tetraethyllead toxicity.[2] It is given by slow injection into a vein or into a muscle.[1]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Calcium disodium versenate, others |
| Other names | edetate calcium disodium, sodium calcium edetate |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | IV, IM |
| Drug class | chelating agent |
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
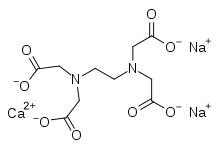
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| E number | E385 (antioxidants, ...) |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.482 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C10H12CaN2Na2O8 |
| Molar mass | 374.270 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
Common side effects include pain at the site of injection.[2] Other side effects may include kidney problems, diarrhea, fever, muscle pains, and low blood pressure.[1] Benefits when needed in pregnancy are likely greater than the risks.[2] Sodium calcium edetate is in the chelating agent family of medication.[2] It is a salt of edetate with two sodium and one calcium atoms.[3] It works by binding a number of heavy metals which allows them to leave the body in the urine.[2]
Sodium calcium edetate came into medical use in the United States in 1953.[2] It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines, the most effective and safe medicines needed in a health system.[4] In the United States a course of treatment costs 50 to 100 USD as of 2015.[5] Edetate disodium is a different formulation which does not have the same effects.[2]
Medical uses
The primarily use is to treat lead poisoning.[1] In lead toxicity it is an alternative to succimer.[2]
It may also be used for plutonium toxicity.[6]
History
Sodium calcium edetate came into medical use in the United States in 1953.[2]
References
- WHO Model Formulary 2008 (PDF). World Health Organization. 2009. p. X. ISBN 9789241547659. Archived (PDF) from the original on 13 December 2016. Retrieved 8 January 2017.
- "Edetate Calcium Disodium". The American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. Archived from the original on 16 January 2017. Retrieved 8 January 2017.
- Kasture, Dr A. V. (2008). Pharmaceutical Chemistry - I. Pragati Books Pvt. Ltd. p. 16.11. ISBN 9788185790121. Archived from the original on 2017-01-16.
- "WHO Model List of Essential Medicines (19th List)" (PDF). World Health Organization. April 2015. Archived (PDF) from the original on 13 December 2016. Retrieved 8 December 2016.
- Hamilton, Richart (2015). Tarascon Pocket Pharmacopoeia 2015 Deluxe Lab-Coat Edition. Jones & Bartlett Learning. p. 471. ISBN 9781284057560.
- Flanagan, Robert; Jones, Alison; Maynard, Robert L. (2003). Antidotes: Principles and Clinical Applications. CRC Press. p. 47. ISBN 9780203485071. Archived from the original on 2017-01-16.