Delapril
Delapril (INN, also known as alindapril) is an ACE inhibitor used as an antihypertensive drug[1] in some European and Asian countries but not in America.[2] It is taken orally, available in 15 mg and 30 mg tablets.[3]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
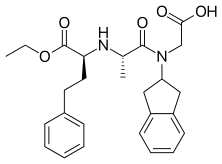
| Formula | C26H32N2O5 |
| Molar mass | 452.542 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| | |
Mechanism
Delapril is a prodrug; it is converted into two active metabolites, 5-hydroxy delapril diacid and delapril diacid. These metabolites bind completely to and inhibit angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE), hence blocking angiotensin I to angiotensin II conversion. The resulting vasodilation prevents the vasoconstrictive effects of angiotensin II. Angiotensin II-induced aldosterone secretion by the adrenal cortex is also decreased by Delapril, leading to increases in excretion of sodium and therefore increases water outflow.[4]
References
- Otero, M. L. (2007). "Manidipine-delapril combination in the management of hypertension". Vascular Health and Risk Management. 3 (3): 255–263. PMC 2293964. PMID 17703633.
- Drugs.com: Delapril
- "cursoenarm.net/UPTODATE/contents/mobipreview.htm?16/0/16396?source=HISTORY". cursoenarm.net. Retrieved 2016-08-28.
- Pubchem. "DELAPRIL | C26H32N2O5 - PubChem". pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved 2016-08-28.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.