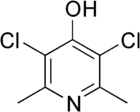
Clopidol
Clopidol is an organic compound that is used as in veterinary medicine as a coccidiostat. It is prepared industrially by a multistep process from dehydroacetic acid.[1]
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Coyden, Clobek(Animate Animal Health) |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.019.099 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C7H7Cl2NO |
| Molar mass | 192.04 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| | |
The US National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health has set a recommended exposure limit (REL) for clopidol at 10 mg/m3 TWA (time-weighted average) for total exposure, 5 mg/m3 TWA for respiratory exposure, and 20 mg/m3 for short-term exposure. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration has set a permissible exposure limit (PEL); the respiratory PEL is the same as the REL, but the total exposure limit is 15 mg/m3.[2]
References
- Raimund Miller, Claudio Abaecherli, Adel Said, Barry Jackson "Ketenes" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, 2001, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. doi: 10.1002/14356007.a15_063
- "Clopidol". Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. NIOSH.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.