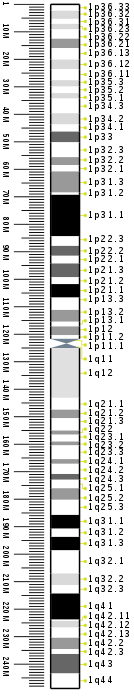
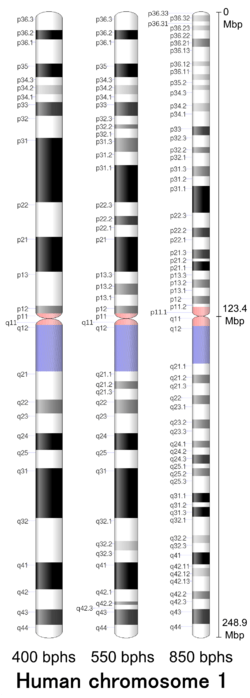
Chromosome 1
Chromosome 1 is the designation for the largest human chromosome. Humans have two copies of chromosome 1, as they do with all of the autosomes, which are the non-sex chromosomes. Chromosome 1 spans about 249 million nucleotide base pairs, which are the basic units of information for DNA.[5] It represents about 8% of the total DNA in human cells.[6]
| Chromosome 1 | |
|---|---|
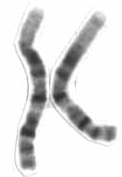 Human chromosome 1 pair after G-banding. One is from mother, one is from father. | |
 Chromosome 1 pair in human male karyogram. | |
| Features | |
| Length (bp) | 248,956,422 bp (GRCh38)[1] |
| No. of genes | 1,961 (CCDS)[2] |
| Type | Autosome |
| Centromere position | Metacentric[3] (123.4 Mbp[4]) |
| Complete gene lists | |
| CCDS | Gene list |
| HGNC | Gene list |
| UniProt | Gene list |
| NCBI | Gene list |
| External map viewers | |
| Ensembl | Chromosome 1 |
| Entrez | Chromosome 1 |
| NCBI | Chromosome 1 |
| UCSC | Chromosome 1 |
| Full DNA sequences | |
| RefSeq | NC_000001 (FASTA) |
| GenBank | CM000663 (FASTA) |
It was the last completed chromosome, sequenced two decades after the beginning of the Human Genome Project.
Genes
Number of genes
The following are some of the gene count estimates of human chromosome 1. Because researchers use different approaches to genome annotation their predictions of the number of genes on each chromosome varies (for technical details, see gene prediction). Among various projects, the collaborative consensus coding sequence project (CCDS) takes an extremely conservative strategy. So CCDS's gene number prediction represents a lower bound on the total number of human protein-coding genes.[7]
| Estimated by | Protein-coding genes | Non-coding RNA genes | Pseudogenes | Source | Release date |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CCDS | 1,961 | — | — | [2] | 2016-09-08 |
| HGNC | 1,993 | 707 | 1,113 | [8] | 2017-05-12 |
| Ensembl | 2,044 | 1,924 | 1,223 | [9] | 2017-03-29 |
| UniProt | 2,064 | — | — | [10] | 2018-02-28 |
| NCBI | 2,093 | 1,790 | 1,426 | [11][12][13] | 2017-05-19 |
Gene list
The following is a partial list of genes on human chromosome 1. For complete list, see the link in the infobox on the right.
- DENN1B hypothesized to be related to asthma
p-arm
Partial list of the genes located on p-arm (short arm) of human chromosome 1:
- AADACL3: Arylacetamide deacetylase-like 3
- AADACL4: Arylacetamide deacetylase-like 4
- ACADM: acyl-Coenzyme A dehydrogenase, C-4 to C-12 straight chain
- ACTL8: Actin-like 8
- ADGRL2 (1p31.1): adhesion G protein-coupled receptor L2
- ADPRHL2: Poly(ADP-ribose) glycohydrolase ARH3
- AMPD2: encoding enzyme AMP deaminase 2
- ARID1A (1p36)
- ATXN7L2: Ataxin 7-like 2
- AZIN2: encoding enzyme Antizyme inhibitor 2 (AzI2) also known as arginine decarboxylase (ADC)
- BCAS2: Breast carcinoma amplified sequence 2
- BCL10 (1p22)
- BCL2L15 (1p13)
- C1orf103: encoding protein Ligand-dependent nuclear receptor-interacting factor 1 (LRIF1)
- C1orf109: chromosome 1 open reading frame 109
- C1orf123: chromosome 1 open reading frame 123
- CACHD1 encoding protein Cache domain containing 1
- CAMTA1 (1p36)
- CASP9 (1p36)
- CASZ1 (1p36): Castor zinc finger 1
- CSDE1: Cold shock domain containing E1
- CHD5 (1p36)
- CLIC4 (1p36)
- CLSPN (1p34)
- CMPK: UMP-CMP kinase
- COL16A1 (1p35)
- COL11A1: collagen, type XI, alpha 1
- CPT2: carnitine palmitoyltransferase II
- CRYZ: Crystallin zeta
- CYP4B1 (1p33)
- CYR61 (1p22)
- DBT: dihydrolipoamide branched chain transacylase E2
- DCLRE1B: DNA cross-link repair 1B
- DEPDC1 encoding protein DEP domain containing 1
- DIRAS3 (1p31): DIRAS family, GTP-binding RAS-like 3
- DPH5: Diphthine synthase
- DVL1 (1p36)
- ENO1 (1p36)
- EPHA2 (1p36)
- EPS15 (1p32)
- ESPN: espin (autosomal recessive deafness 36)
- EVI5: ecotropic viral integration site 5
- EXTL1: exostosin like glycosyltransferase 1
- EXTL2: exostosin like glycosyltransferase 2
- FAM46B: family with sequence similarity 46, member B
- FAM46C: family with sequence similarity 46, member C
- FAM76A: family with sequence similarity 76, member A
- FBXO2: F-box protein 2
- FNBP1L encoding protein Formin-binding protein 1-like
- FPGT: Fucose-1-phosphate guanylyltransferase
- FUBP1 (1p31)
- GALE: UDP-galactose-4-epimerase
- GADD45A (1p31)
- GBP1 (1p22)
- GBP2: guanylate binding protein 2
- GBP5 encoding protein Guanylate binding protein 5
- GJB3: gap junction protein, beta 3, 31kDa (connexin 31)
- GLMN (1p22)
- GNL2: G protein nucleolar 2
- GSTM1 (1p13)
- HDAC1 (1p35)
- HES2: Hes family bHLH transcription factor 2
- HES3: Hes family bHLH transcription factor 3
- HMGCL: 3-hydroxymethyl-3-methylglutaryl-Coenzyme A lyase (hydroxymethylglutaricaciduria)
- HAO2 encoding protein Hydroxyacid oxidase 2
- HMGCS2: 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA synthase 2
- HP1BP3: Heterochromatin protein 1, binding protein 3
- IFI6: Interferon alpha-inducible protein 6
- IL22RA1 (1p36)
- INTS11: Integrator complex subunit 11
- JAK1 (1p31)
- JUN (1p32)
- KCNQ4: potassium voltage-gated channel, KQT-like subfamily, member 4
- KIF1B: kinesin family member 1B
- L1TD1: LINE-1 type transposase domain containing 1
- LCK (1p35)
- LRRC39: Leucine-rich repeat-containing protein 39
- LRRC40: Leucine-rich repeat-containing protein 40
- LRRC41: Leucine-rich repeat-containing protein 41
- LRRC8D: Leucine-rich repeat-containing protein 8D
- MAN1A2: Mannosyl-oligosaccharide 1,2-alpha-mannosidase IB
- MEAF6: MYST/ESA1 associated factor 6
- MECR: Trans-2-enoyl-CoA reductase, mitochondrial
- MFAP2: Microfibrillar-associated protein 2
- MIB2 (1p36)
- MIER1 (1p31)
- MFN2: mitofusin 2
- MFSD2: Major facilitator superfamily domain containing 2A
- MIR6079: microRNA 6079
- MMEL1: Membrane metallo-endopeptidase-like 1
- MTFR1L: mitochondrial fission regulator 1 like
- MTHFR (1p36): 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (NADPH)
- MUL1: Mitochondrial E3 ubiquitin protein ligase 1
- MUTYH (1p34): mutY homolog (E. coli)
- NBPF3: Neuroblastoma breakpoint family member 3
- NGF: Nerve Growth Factor
- NOL9: Nucleolar protein 9
- NRAS (1p13)
- NOTCH2 (1p12)
- OLFML3: Olfactomedin-like 3
- OMA1: Metalloendopeptidase OMA1, mitochondrial
- OVGP1: Oviductal glycoprotein 1
- PARK7 (1p36): Parkinson disease (autosomal recessive, early onset) 7
- PINK1: PTEN induced putative kinase 1
- PLOD1: procollagen-lysine 1, 2-oxoglutarate 5-dioxygenase 1
- PRMT6: Protein arginine methyltransferase 6
- PSRC1: Proline/serine-rich coiled-coil protein 1
- RAD54L: RAD54-like
- RAP1A (1p13)
- RBM15 (1p13)
- RCC2: Regulator of chromosome condensation 2
- REG4 (1p12)
- RHBDL2: Rhomboid like 2
- RHOC (1p13)
- RLF: rearranged L-myc fusion
- RNF11 (1p32)
- RNF220: RING finger protein 220
- RPA2 (1p35)
- RSPO1 (1p34)
- S100A1 (1q21)
- SDC3: Syndecan-3
- SDHB (1p36)
- SFPQ (1p34)
- SGIP1: SH3 domain GRB2-like protein 3-interaction protein 1
- SH3BGRL3: SH3 domain-binding glutamic acid-rich-like protein 3
- SLC16A1 (1p13)
- SPSB1: SPRY domain-containing SOCS box protein 1
- STIL (1p33)
- SYCP1: Synaptonemal complex protein 1
- SZT2: Seizure threshold 2 homolog
- TACSTD2: tumor-associated calcium signal transducer 2
- TAL1 (1p33)
- TCEB3: Transcription elongation factor B polypeptide 3
- TGFBR3 (1p22)
- THRAP3 (1p34)
- TIE1 (1p34)
- TMCO4: encoding protein transmembrane and coiled-coil domains 4
- TMEM48: encoding protein nucleoporin NDC1
- TMEM50A: Transmembrane protein 50A
- TMEM59: Transmembrane protein 59
- TMEM69: Transmembrane protein 69
- TMEM201 encoding protein Transmembrane protein 201
- TMEM222: Transmembrane protein 222
- TOE1: Target of EGR1 protein 1
- TRAPPC3: Trafficking protein particle complex subunit 3
- TRIT1: tRNA isopentenyltransferase, mitochondrial
- TSHB: thyroid stimulating hormone, beta
- TTC39A: Tetratricopeptide repeat 39A
- UBR4: E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase component n-recognin 4
- UROD: uroporphyrinogen decarboxylase (the gene for porphyria cutanea tarda)
- USP1 (1p31)
- USP48: Ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase 48
- VAV3 (1p13)
- VPS13D: Vacuolar protein sorting-associated protein 13D
- VTCN1 (1p13)
- WARS2: Tryptophanyl-tRNA synthetase, mitochondrial
- WDR77 (1p13)
- YBX1 (1p34)
- ZCCHC17: zinc finger CCHC-type containing 17
- ZMYM1 encoding protein Zinc finger MYM-type containing 1
- ZNF436: Zinc finger protein 436
- ZYG11B encoding protein Zyg-11 family member B, cell cycle regulator
- ZZZ3: ZZ-type zinc finger-containing protein 3
q-arm
Partial list of the genes located on q-arm (long arm) of human chromosome 1:
- ABL2 (1q25)
- ADIPOR1 (1q32)
- AHCTF1: encoding protein ELYS
- AKT3 (1q43-44)
- ANGPTL1: Angiopoietin-related protein 1
- ARHGEF2 (1q22)
- ARID4B: encoding protein AT-rich interactive domain-containing protein 4B
- ARV1 encoding protein ARV1 homolog (S. cerevisiae)
- ARNT (1q21)
- ASPM (1q31): a brain size determinant
- ATF3 (1q32)
- ATP2B4 (1q32)
- BCL9 (1q21)
- C1orf21: chromosome 1 open reading frame 21
- C1orf35 encoding protein Chromosome 1 open reading frame 35
- C1orf49: chromosome 1 open reading frame 49
- C1orf74: chromosome 1 open reading frame 74
- C2CD4D: C2 calcium-dependent domain-containing 4D
- CD5L: CD5 molecule like
- CENPL: Centromere protein L
- CENPF (1q41)
- CHTOP: Chromatin target of prmt1
- CNIH4: cornichon homolog 4
- CNST: Consortin
- CREG1: Cellular repressor of E1A stimulated genes 1
- CRP: C-reactive protein
- CRTC2 (1q21)
- CSRP1: Cysteine and glycine rich protein 1
- DDX59: DEAD-box helicase 59
- DPT: Dermatopontin
- DISC2, long non-coding RNA
- DUSP10 (1q41)
- DNAH14 encoding protein Dynein, axonemal, heavy chain 14
- ECM1 (1q21)
- EDEM3: ER degradation enhancing alpha-mannosidase like protein 3
- EGLN1 (1q42)
- ENAH (1q42)
- ESRRG (1q41)
- FAM20B: FAM20B, glycosaminoglycan xylosylkinase
- FAM63A: Family with sequence similarity 63, member A
- FAM78B: family with sequence similarity 78, member B
- FAM129A: family with sequence similarity 129, member A
- FBXO28: F-box protein 28
- FCMR: Fc fragment of IgM receptor
- FCGR2B (1q23)
- FH (1q43)
- FMO3: flavin containing monooxygenase 3
- FRA1J encoding protein Fragile site, 5-azacytidine type, common, fra(1)(q12)
- GAS5 (1q25)
- GBA: glucosidase, beta; acid (includes glucosylceramidase) (gene for Gaucher disease)
- GBAP1: glucosylceramidase beta pseudogene 1
- GLC1A: gene for glaucoma
- GON4L: gon-4 like
- GPA33 (1q24)
- GPR37L1 G protein-coupled receptor 37 like 1
- HEATR1: HEAT repeat-containing protein 1
- HFE2: hemochromatosis type 2 (juvenile)
- HIST2H2AB: Histone 2A type 2-B
- HIST2H2BF: Histone H2B type 2-F
- HIST2H3PS2: Histone cluster 2, H3, pseudogene 2
- HIST3H2A: Histone H2A type 3
- HIST3H2BB: Histone H2B type 3-B
- HPC1: gene for prostate cancer
- IGSF8 (1q23)
- INAVA: Innate immunity activator protein
- INTS3: Integrator complex subunit 3
- IRF6: gene for connective tissue formation
- KCNH1 (1q32)
- KIF14 (1q32)
- LEFTY1: Left-right determination factor 1
- LHX9 encoding protein LIM homeobox 9
- LMNA: lamin A/C
- LOC645166 encoding protein Lymphocyte-specific protein 1 pseudogene
- LYPLAL1: Lysophospholipase-like 1
- MAPKAPK2 (1q32)
- MIR194-1: microRNA 194-1
- MIR5008: microRNA 5008
- MPC2: Mitochondrial pyruvate carrier 2
- MOSC1: MOCO sulphurase C-terminal domain containing 1
- MOSC2: MOSC domain-containing protein 2, mitochondrial
- MPZ: myelin protein zero (Charcot–Marie–Tooth neuropathy 1B)
- MSTO1: misato 1
- MTR: 5-methyltetrahydrofolate-homocysteine methyltransferase
- NAV1: Neuron navigator 1
- NBPF16: Neuroblastoma breakpoint family, member 16
- NOC2L: Nucleolar complex protein 2 homolog
- NUCKS1: Nuclear ubiquitous casein and cyclin-dependent kinases substrate
- NVL: Nuclear valosin-containing protein-like
- OLFML2B: Olfactomedin-like 2B
- OPTC: Opticin
- OTUD7B: OTU domain-containing protein 7B
- PACERR encoding protein PTGS2 antisense NFKB1 complex-mediated expression regulator RNA
- PBX1 (1q23)
- PEA15 (1q23)
- PGDB5: PiggyBac transposable element derived 5
- PIAS3 (1q21)
- PI4KB: Phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase beta
- PIP5K1A (1q21): Phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate 5-kinase type-1 alpha
- PLA2G4A (1q31)
- PPOX: protoporphyrinogen oxidase
- PRCC (1q23)
- PRR9 encoding protein Proline rich 9
- PSEN2 (1q42): presenilin 2 (Alzheimer disease 4)
- PTGS2 (1q31)
- PTPN14 (1q32-41)
- PTPN7 (1q32)
- RABIF: RAB interacting factor
- RASSF5 (1q32)
- RGS2 (1q31)
- RN5S1@: RNA, 5S ribosomal 1q42 cluster
- RPS27 (1q21)
- SCAMP3: Secretory carrier-associated membrane protein 3
- SDHC (1q23)
- SELE (1q24)
- SHC1 (1q21)
- SLC39A1 (1q21)
- SLC50A1: Solute carrier family 50 member 1
- SMCP: Sperm mitochondrial-associated cysteine-rich protein
- SMG7: nonsense mediated mRNA decay factor
- SMYD3 (1q44)
- SPG23
- SPRR1A: Cornifin-A
- SPRR1B: Cornifin-B
- SPRR2A: Small proline rich protein 2A
- SPRTN: Spartan
- TARBP1: TAR (HIV-1) RNA-binding protein 1
- TBCE: Tubulin-specific chaperone E
- THBS3: Thrombospondin 3
- TMCO1: Transmembrane and coiled-coil domain-containing protein 1
- TMEM9: Transmembrane protein 9
- TMEM63A: Transmembrane protein 63A
- TNFSF18 (1q25)
- TNN (1q25)
- TNNT2: cardiac troponin T2
- TOR1AIP1: Torsin-1A-interacting protein 1
- TP53BP2 (1q41)
- TRE-CTC1-5: Transfer RNA-Glu (CTC) 1-5
- TRP (1q31)
- UAP1: UDP-N-acetylhexosamine pyrophosphorylase
- USH2A: Usher syndrome 2A (autosomal recessive, mild)
- USF1 (1q23)
- VPS45: Vacuolar protein sorting-associated protein 45
- VPS72: Vacuolar protein sorting-associated protein 72
- YY1AP1: YY1-associated protein 1
- ZBED6: zinc finger, BED-type containing 6
- ZC3H11A: Zinc finger CCCH domain-containing protein 11A
- ZNF687: Zinc finger protein 687
- ZNF648 encoding protein Zinc finger protein 648
- ZNF695: Zinc finger protein 695
Diseases and disorders
There are 890 known diseases related to this chromosome. Some of these diseases are hearing loss, Alzheimer's disease, glaucoma and breast cancer. Rearrangements and mutations of chromosome 1 are prevalent in cancer and many other diseases. Patterns of sequence variation reveal signals of recent selection in specific genes that may contribute to human fitness, and also in regions where no function is evident.
Complete monosomy (only having one copy of the entire chromosome) is invariably lethal before birth.[14] Complete trisomy (having three copies of the entire chromosome) is lethal within days after conception.[14] Some partial deletions and partial duplications produce birth defects.
The following diseases are some of those related to genes on chromosome 1 (which contains the most known genetic diseases of any human chromosome):
- 1q21.1 deletion syndrome
- 1q21.1 duplication syndrome
- Alzheimer's disease
- Breast cancer
- Brooke Greenberg Disease (Syndrome X)
- Carnitine palmitoyltransferase II deficiency
- Charcot–Marie–Tooth disease, types 1 and 2
- collagenopathy, types II and XI
- congenital hypothyroidism
- Ehlers-Danlos syndrome
- Factor V Leiden thrombophilia
- Familial adenomatous polyposis
- galactosemia
- Gaucher disease
- Gaucher-like disease
- Gelatinous drop-like corneal dystrophy
- Glaucoma
- Hearing loss, autosomal recessive deafness 36
- Hemochromatosis
- Hepatoerythropoietic porphyria
- Homocystinuria
- Hutchinson Gilford progeria syndrome
- 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA lyase deficiency
- Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, autosomal dominant mutations of TNNT2; hypertrophy usually mild; restrictive phenotype may be present; may carry high risk of sudden cardiac death
- maple syrup urine disease
- medium-chain acyl-coenzyme A dehydrogenase deficiency
- Microcephaly
- Muckle-Wells Syndrome
- Nonsyndromic deafness
- Oligodendroglioma
- Parkinson disease
- Pheochromocytoma
- porphyria
- porphyria cutanea tarda
- popliteal pterygium syndrome
- prostate cancer
- Stickler syndrome
- TAR syndrome
- trimethylaminuria
- Usher syndrome
- Usher syndrome type II
- Van der Woude syndrome
- Variegate porphyria
Cytogenetic band
| Chr. | Arm[20] | Band[21] | ISCN start[22] |
ISCN stop[22] |
Basepair start |
Basepair stop |
Stain[23] | Density |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | p | 36.33 | 0 | 100 | 1 | 2,300,000 | gneg | |
| 1 | p | 36.32 | 100 | 244 | 2,300,001 | 5,300,000 | gpos | 25 |
| 1 | p | 36.31 | 244 | 344 | 5,300,001 | 7,100,000 | gneg | |
| 1 | p | 36.23 | 344 | 459 | 7,100,001 | 9,100,000 | gpos | 25 |
| 1 | p | 36.22 | 459 | 660 | 9,100,001 | 12,500,000 | gneg | |
| 1 | p | 36.21 | 660 | 861 | 12,500,001 | 15,900,000 | gpos | 50 |
| 1 | p | 36.13 | 861 | 1206 | 15,900,001 | 20,100,000 | gneg | |
| 1 | p | 36.12 | 1206 | 1321 | 20,100,001 | 23,600,000 | gpos | 25 |
| 1 | p | 36.11 | 1321 | 1521 | 23,600,001 | 27,600,000 | gneg | |
| 1 | p | 35.3 | 1521 | 1651 | 27,600,001 | 29,900,000 | gpos | 25 |
| 1 | p | 35.2 | 1651 | 1780 | 29,900,001 | 32,300,000 | gneg | |
| 1 | p | 35.1 | 1780 | 1895 | 32,300,001 | 34,300,000 | gpos | 25 |
| 1 | p | 34.3 | 1895 | 2210 | 34,300,001 | 39,600,000 | gneg | |
| 1 | p | 34.2 | 2210 | 2411 | 39,600,001 | 43,700,000 | gpos | 25 |
| 1 | p | 34.1 | 2411 | 2770 | 43,700,001 | 46,300,000 | gneg | |
| 1 | p | 33 | 2770 | 2986 | 46,300,001 | 50,200,000 | gpos | 75 |
| 1 | p | 32.3 | 2986 | 3273 | 50,200,001 | 55,600,000 | gneg | |
| 1 | p | 32.2 | 3273 | 3416 | 55,600,001 | 58,500,000 | gpos | 50 |
| 1 | p | 32.1 | 3416 | 3732 | 58,500,001 | 60,800,000 | gneg | |
| 1 | p | 31.3 | 3732 | 3976 | 60,800,001 | 68,500,000 | gpos | 50 |
| 1 | p | 31.2 | 3976 | 4206 | 68,500,001 | 69,300,000 | gneg | |
| 1 | p | 31.1 | 4206 | 4852 | 69,300,001 | 84,400,000 | gpos | 100 |
| 1 | p | 22.3 | 4852 | 5210 | 84,400,001 | 87,900,000 | gneg | |
| 1 | p | 22.2 | 5210 | 5440 | 87,900,001 | 91,500,000 | gpos | 75 |
| 1 | p | 22.1 | 5440 | 5741 | 91,500,001 | 94,300,000 | gneg | |
| 1 | p | 21.3 | 5741 | 5957 | 94,300,001 | 99,300,000 | gpos | 75 |
| 1 | p | 21.2 | 5957 | 6029 | 99,300,001 | 101,800,000 | gneg | |
| 1 | p | 21.1 | 6029 | 6244 | 101,800,001 | 106,700,000 | gpos | 100 |
| 1 | p | 13.3 | 6244 | 6459 | 106,700,001 | 111,200,000 | gneg | |
| 1 | p | 13.2 | 6459 | 6660 | 111,200,001 | 115,500,000 | gpos | 50 |
| 1 | p | 13.1 | 6660 | 6861 | 115,500,001 | 117,200,000 | gneg | |
| 1 | p | 12 | 6861 | 7048 | 117,200,001 | 120,400,000 | gpos | 50 |
| 1 | p | 11.2 | 7048 | 7119 | 120,400,001 | 121,700,000 | gneg | |
| 1 | p | 11.1 | 7119 | 7335 | 121,700,001 | 123,400,000 | acen | |
| 1 | q | 11 | 7335 | 7579 | 123,400,001 | 125,100,000 | acen | |
| 1 | q | 12 | 7579 | 8483 | 125,100,001 | 143,200,000 | gvar | |
| 1 | q | 21.1 | 8483 | 8756 | 143,200,001 | 147,500,000 | gneg | |
| 1 | q | 21.2 | 8756 | 8957 | 147,500,001 | 150,600,000 | gpos | 50 |
| 1 | q | 21.3 | 8957 | 9244 | 150,600,001 | 155,100,000 | gneg | |
| 1 | q | 22 | 9244 | 9459 | 155,100,001 | 156,600,000 | gpos | 50 |
| 1 | q | 23.1 | 9459 | 9832 | 156,600,001 | 159,100,000 | gneg | |
| 1 | q | 23.2 | 9832 | 10048 | 159,100,001 | 160,500,000 | gpos | 50 |
| 1 | q | 23.3 | 10048 | 10349 | 160,500,001 | 165,500,000 | gneg | |
| 1 | q | 24.1 | 10349 | 10507 | 165,500,001 | 167,200,000 | gpos | 50 |
| 1 | q | 24.2 | 10507 | 10679 | 167,200,001 | 170,900,000 | gneg | |
| 1 | q | 24.3 | 10679 | 10894 | 170,900,001 | 173,000,000 | gpos | 75 |
| 1 | q | 25.1 | 10894 | 11009 | 173,000,001 | 176,100,000 | gneg | |
| 1 | q | 25.2 | 11009 | 11196 | 176,100,001 | 180,300,000 | gpos | 50 |
| 1 | q | 25.3 | 11196 | 11598 | 180,300,001 | 185,800,000 | gneg | |
| 1 | q | 31.1 | 11598 | 11827 | 185,800,001 | 190,800,000 | gpos | 100 |
| 1 | q | 31.2 | 11827 | 11942 | 190,800,001 | 193,800,000 | gneg | |
| 1 | q | 31.3 | 11942 | 12172 | 193,800,001 | 198,700,000 | gpos | 100 |
| 1 | q | 32.1 | 12172 | 12617 | 198,700,001 | 207,100,000 | gneg | |
| 1 | q | 32.2 | 12617 | 12803 | 207,100,001 | 211,300,000 | gpos | 25 |
| 1 | q | 32.3 | 12803 | 13033 | 211,300,001 | 214,400,000 | gneg | |
| 1 | q | 41 | 13033 | 13320 | 214,400,001 | 223,900,000 | gpos | 100 |
| 1 | q | 42.11 | 13320 | 13406 | 223,900,001 | 224,400,000 | gneg | |
| 1 | q | 42.12 | 13406 | 13607 | 224,400,001 | 226,800,000 | gpos | 25 |
| 1 | q | 42.13 | 13607 | 13966 | 226,800,001 | 230,500,000 | gneg | |
| 1 | q | 42.2 | 13966 | 14153 | 230,500,001 | 234,600,000 | gpos | 50 |
| 1 | q | 42.3 | 14153 | 14397 | 234,600,001 | 236,400,000 | gneg | |
| 1 | q | 43 | 14397 | 14756 | 236,400,001 | 243,500,000 | gpos | 75 |
| 1 | q | 44 | 14756 | 15100 | 243,500,001 | 248,956,422 | gneg |
References
- "Human Genome Assembly GRCh38 - Genome Reference Consortium". National Center for Biotechnology Information. 2013-12-24. Retrieved 2017-03-04.
- "Search results - 1[CHR] AND "Homo sapiens"[Organism] AND ("has ccds"[Properties] AND alive[prop]) - Gene". NCBI. CCDS Release 20 for Homo sapiens. 2016-09-08. Retrieved 2017-05-28.
- Tom Strachan; Andrew Read (2 April 2010). Human Molecular Genetics. Garland Science. p. 45. ISBN 978-1-136-84407-2.
- Genome Decoration Page, NCBI. Ideogram data for Homo sapience (850 bphs, Assembly GRCh38.p3). Last update 2014-06-03. Retrieved 2017-04-26.
- http://vega.sanger.ac.uk/Homo_sapiens/mapview?chr=1 Chromosome size and number of genes derived from this database, retrieved 2012-03-11.
- Gregory SG, Barlow KF, McLay KE, Kaul R, Swarbreck D, Dunham A, et al. (May 2006). "The DNA sequence and biological annotation of human chromosome 1". Nature. 441 (7091): 315–21. doi:10.1038/nature04727. PMID 16710414.
- Pertea M, Salzberg SL (2010). "Between a chicken and a grape: estimating the number of human genes". Genome Biol. 11 (5): 206. doi:10.1186/gb-2010-11-5-206. PMC 2898077. PMID 20441615.
- "Statistics & Downloads for chromosome 1". HUGO Gene Nomenclature Committee. 2017-05-12. Retrieved 2017-05-19.
- "Chromosome 1: Chromosome summary - Homo sapiens". Ensembl Release 88. 2017-03-29. Retrieved 2017-05-19.
- "Human chromosome 1: entries, gene names and cross-references to MIM". UniProt. 2018-02-28. Retrieved 2018-03-16.
- "Search results - 1[CHR] AND "Homo sapiens"[Organism] AND ("genetype protein coding"[Properties] AND alive[prop]) - Gene". NCBI. 2017-05-19. Retrieved 2017-05-20.
- "Search results - 1[CHR] AND "Homo sapiens"[Organism] AND ( ("genetype miscrna"[Properties] OR "genetype ncrna"[Properties] OR "genetype rrna"[Properties] OR "genetype trna"[Properties] OR "genetype scrna"[Properties] OR "genetype snrna"[Properties] OR "genetype snorna"[Properties]) NOT "genetype protein coding"[Properties] AND alive[prop]) - Gene". NCBI. 2017-05-19. Retrieved 2017-05-20.
- "Search results - 1[CHR] AND "Homo sapiens"[Organism] AND ("genetype pseudo"[Properties] AND alive[prop]) - Gene". NCBI. 2017-05-19. Retrieved 2017-05-20.
- Gersen, Steven L.; Keagle, Martha B. (2013-03-26). The Principles of Clinical Cytogenetics. Springer Science & Business Media. p. 278. ISBN 9781441916884.
- Genome Decoration Page, NCBI. Ideogram data for Homo sapience (400 bphs, Assembly GRCh38.p3). Last update 2014-03-04. Retrieved 2017-04-26.
- Genome Decoration Page, NCBI. Ideogram data for Homo sapience (550 bphs, Assembly GRCh38.p3). Last update 2015-08-11. Retrieved 2017-04-26.
- International Standing Committee on Human Cytogenetic Nomenclature (2013). ISCN 2013: An International System for Human Cytogenetic Nomenclature (2013). Karger Medical and Scientific Publishers. ISBN 978-3-318-02253-7.
- Sethakulvichai, W.; Manitpornsut, S.; Wiboonrat, M.; Lilakiatsakun, W.; Assawamakin, A.; Tongsima, S. (2012). "Estimation of band level resolutions of human chromosome images" (PDF). In Computer Science and Software Engineering (JCSSE), 2012 International Joint Conference on: 276–282. doi:10.1109/JCSSE.2012.6261965.
- Genome Decoration Page, NCBI. Ideogram data for Homo sapience (850 bphs, Assembly GRCh38.p3). Last update 2014-06-03. Retrieved 2017-04-26.
- "p": Short arm; "q": Long arm.
- For cytogenetic banding nomenclature, see article locus.
- These values (ISCN start/stop) are based on the length of bands/ideograms from the ISCN book, An International System for Human Cytogenetic Nomenclature (2013). Arbitrary unit.
- gpos: Region which is positively stained by G banding, generally AT-rich and gene poor; gneg: Region which is negatively stained by G banding, generally CG-rich and gene rich; acen Centromere. var: Variable region; stalk: Stalk.
Further reading
- Murphy WJ, Fronicke L, O'Brien SJ, Stanyon R (2003). "The Origin of Human Chromosome 1 and Its Homologs in Placental Mammals". Genome Res. 13 (8): 1880–8. doi:10.1101/gr.1022303. PMC 403779. PMID 12869576.
- Revera, M.; Van Der Merwe, L; et al. (2007). "Long-term follow-up of R403WMHY7 and R92WTNNT2 HCM families: mutations determine left ventricular dimensions but not wall thickness during disease progression". Cardiovascular Journal of Africa. 18 (3): 146–153. PMC 4213759. PMID 17612745.
- Schutte BC, Carpten JD, Forus A, Gregory SG, Horii A, White PS (2001). "Report and abstracts of the sixth international workshop on human chromosome 1 mapping 2000. Iowa City, Iowa, USA. 30 September-3 October 2000". Cytogenet Cell Genet. 92 (1–2): 23–41. doi:10.1159/000056867. PMID 11306795.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Human chromosome 1. |
- National Institutes of Health. "Chromosome 1". Genetics Home Reference. Retrieved 2017-05-06.
- "Final genome 'chapter' published". BBC NEWS. 2006-05-18. Retrieved 2017-05-06.
- "Chromosome 1". Human Genome Project Information Archive 1990–2003. Retrieved 2017-05-06.