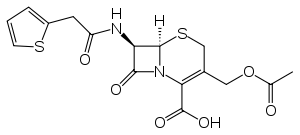
Cefalotin
Cefalotin (INN) /ˌsɛfəˈloʊtɪn/ or cephalothin (USAN) /ˌsɛfəˈloʊθɪn/ is a first-generation cephalosporin antibiotic.[1] It was the first cephalosporin marketed (1964) and continues to be widely used.[2] It is an intravenously administered agent with a similar antimicrobial spectrum to cefazolin and the oral agent cefalexin. Cefalotin sodium is marketed as Keflin (Lilly) and under other trade names.[3]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| MedlinePlus | a682860 |
| Pregnancy category | |
| Routes of administration | Intravenous |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | n/a |
| Protein binding | 65 to 80% |
| Metabolism | Hepatic |
| Elimination half-life | 30 minutes to 1 hour |
| Excretion | Renal |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.005.288 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C16H16N2O6S2 |
| Molar mass | 396.44 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 160 to 160.5 °C (320.0 to 320.9 °F) |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| (verify) | |
References
- Hameed, T. K.; Robinson, J. L. (2002). "Review of the use of cephalosporins in children with anaphylactic reactions from penicillins". The Canadian Journal of Infectious Diseases. 13 (4): 253–8. PMC 2094874. PMID 18159398.
- David Greenwood (21 February 2008). Antimicrobial Drugs: Chronicle of a Twentieth Century Medical Triumph. OUP Oxford. pp. 128–. ISBN 978-0-19-953484-5.
- International Drug Names: Cefalotin
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.