Carboxypeptidase B2
Carboxypeptidase B2 (CPB2), also known as carboxypeptidase U (CPU), plasma carboxypeptidase B (pCPB) or thrombin-activatable fibrinolysis inhibitor (TAFI), is an enzyme that, in humans, is encoded by the gene CPB2.[5][6]
Function
CPB2 is synthesized by the liver[7] and circulates in the plasma as a plasminogen-bound zymogen. When it is activated by proteolysis at residue Arg92 by the thrombin/thrombomodulin complex, CPB2 exhibits carboxypeptidase activity. Activated CPB2 reduces fibrinolysis by removing the fibrin C-terminal residues that are important for the binding and activation of plasminogen.[8][9]
Carboxypeptidases are enzymes that hydrolyze C-terminal peptide bonds. The carboxypeptidase family includes metallo-, serine, and cysteine carboxypeptidases. According to their substrate specificity, these enzymes are referred to as carboxypeptidase A (cleaving aliphatic residues) or carboxypeptidase B (cleaving basic amino residues). The protein encoded by this gene is activated by thrombin and acts on carboxypeptidase B substrates. After thrombin activation, the mature protein downregulates fibrinolysis.[10]
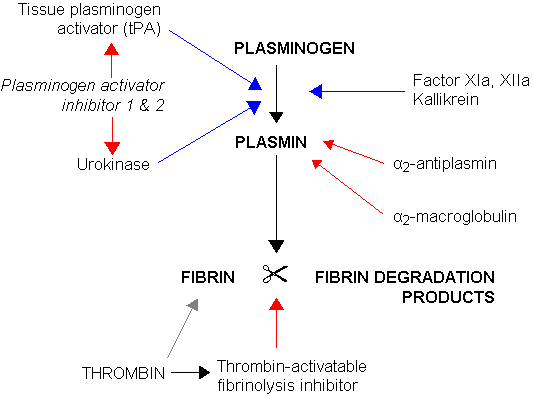 Fibrinolysis (simplified). Blue arrows denote stimulation, and red arrows inhibition. |
Isozymes
Polymorphisms have been described for this gene and its promoter region. Available sequence data analyses indicate splice variants that encode different isoforms.[10]
See also
- Carboxypeptidase B
References
- GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000080618 - Ensembl, May 2017
- GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000021999 - Ensembl, May 2017
- "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- Eaton DL, Malloy BE, Tsai SP, Henzel W, Drayna D (Dec 1991). "Isolation, molecular cloning, and partial characterization of a novel carboxypeptidase B from human plasma". J Biol Chem. 266 (32): 21833–8. PMID 1939207.
- Tsai SP, Drayna D (Dec 1992). "The gene encoding human plasma carboxypeptidase B (CPB2) resides on chromosome 13". Genomics. 14 (2): 549–50. doi:10.1016/S0888-7543(05)80268-X. PMID 1427879.
- Kaushansky K, Lichtman M, Beutler E, Kipps T, Prchal J, Seligsohn U. (2010; edition 8: pages 1833-1834 and 2040-2041) Williams Hematology. McGraw-Hill. ISBN 978-0071621519
- Zhao L, Morser J, Bajzar L, Nesheim M, Nagashima M (December 1998). "Identification and characterization of two thrombin-activatable fibrinolysis inhibitor isoforms". Thromb. Haemost. 80 (6): 949–55. PMID 9869166.
- Boffa MB, Reid TS, Joo E, Nesheim ME, Koschinsky ML (May 1999). "Characterization of the gene encoding human TAFI (thrombin-activable fibrinolysis inhibitor; plasma procarboxypeptidase B)". Biochemistry. 38 (20): 6547–58. doi:10.1021/bi990229v. PMID 10350473.
- "Entrez Gene: CPB2 carboxypeptidase B2 (plasma)".
Further reading
- Bouma BN, Mosnier LO (2005). "Thrombin activatable fibrinolysis inhibitor (TAFI) at the interface between coagulation and fibrinolysis". Pathophysiol. Haemost. Thromb. 33 (5–6): 375–81. doi:10.1159/000083832. PMID 15692247.
- Marinkovic DV, Marinkovic JN, Erdös EG, Robinson CJ (1977). "Purification of carboxypeptidase B from human pancreas". Biochem. J. 163 (2): 253–60. PMC 1164691. PMID 17398.
- Pascual R, Burgos FJ, Salva M, et al. (1989). "Purification and properties of five different forms of human procarboxypeptidases". Eur. J. Biochem. 179 (3): 609–16. doi:10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14590.x. PMID 2920728.
- Valnickova Z, Thogersen IB, Christensen S, et al. (1996). "Activated human plasma carboxypeptidase B is retained in the blood by binding to alpha2-macroglobulin and pregnancy zone protein". J. Biol. Chem. 271 (22): 12937–43. doi:10.1074/jbc.271.22.12937. PMID 8662763.
- Bajzar L, Morser J, Nesheim M (1996). "TAFI, or plasma procarboxypeptidase B, couples the coagulation and fibrinolytic cascades through the thrombin-thrombomodulin complex". J. Biol. Chem. 271 (28): 16603–8. doi:10.1074/jbc.271.28.16603. PMID 8663147.
- Vanhoof G, Wauters J, Schatteman K, et al. (1997). "The gene for human carboxypeptidase U (CPU)--a proposed novel regulator of plasminogen activation--maps to 13q14.11". Genomics. 38 (3): 454–5. doi:10.1006/geno.1996.0656. PMID 8975730.
- Matsumoto A, Itoh K, Matsumoto R (2000). "A novel carboxypeptidase B that processes native beta-amyloid precursor protein is present in human hippocampus". Eur. J. Neurosci. 12 (1): 227–38. doi:10.1046/j.1460-9568.2000.00908.x. PMID 10651877.
- Marx PF, Hackeng TM, Dawson PE, et al. (2000). "Inactivation of active thrombin-activable fibrinolysis inhibitor takes place by a process that involves conformational instability rather than proteolytic cleavage". J. Biol. Chem. 275 (17): 12410–5. doi:10.1074/jbc.275.17.12410. PMID 10777524.
- Mosnier LO, Lisman T, van den Berg HM, et al. (2002). "The defective down regulation of fibrinolysis in haemophilia A can be restored by increasing the TAFI plasma concentration". Thromb. Haemost. 86 (4): 1035–9. PMID 11686321.
- Mosnier LO, Meijers JC, Bouma BN (2002). "The role of protein S in the activation of thrombin activatable fibrinolysis inhibitor (TAFI) and regulation of fibrinolysis". Thromb. Haemost. 86 (4): 1040–6. PMID 11686322.
- Mosnier LO, Elisen MG, Bouma BN, Meijers JC (2002). "Protein C inhibitor regulates the thrombin-thrombomodulin complex in the up- and down regulation of TAFI activation". Thromb. Haemost. 86 (4): 1057–64. PMID 11686324.
- Morange PE, Aillaud MF, Nicaud V, et al. (2002). "Ala147Thr and C+1542G polymorphisms in the TAFI gene are not associated with a higher risk of venous thrombosis in FV Leiden carriers". Thromb. Haemost. 86 (6): 1583–4. PMID 11776333.
- Schneider M, Nagashima M, Knappe S, et al. (2002). "Amino acid residues in the P6-P'3 region of thrombin-activable fibrinolysis inhibitor (TAFI) do not determine the thrombomodulin dependence of TAFI activation". J. Biol. Chem. 277 (12): 9944–51. doi:10.1074/jbc.M111685200. PMID 11786552.
- Koschinsky ML, Boffa MB, Nesheim ME, et al. (2002). "Association of a single nucleotide polymorphism in CPB2 encoding the thrombin-activable fibrinolysis inhibitor (TAF1) with blood pressure". Clin. Genet. 60 (5): 345–9. doi:10.1034/j.1399-0004.2001.600504.x. PMID 11903334.
- Yano Y, Gabazza EC, Hori Y, et al. (2002). "Association between plasma thrombin-activatable fibrinolysis inhibitor levels and activated protein C in normotensive type 2 diabetic patients". Diabetes Care. 25 (7): 1245–6. doi:10.2337/diacare.25.7.1245. PMID 12087030.
- Antovic JP, Blombäck M (2003). "Thrombin-activatable fibrinolysis inhibitor antigen and TAFI activity in patients with APC resistance caused by factor V Leiden mutation". Thromb. Res. 106 (1): 59–62. doi:10.1016/S0049-3848(02)00072-5. PMID 12165290.
This article incorporates text from the United States National Library of Medicine, which is in the public domain.