Ball-and-socket joint
The ball and socket joint (or spheroid joint) is a type of synovial joint in which the ball-shaped surface of one rounded bone fits into the cup-like depression of another bone. The distal bone is capable of motion around an indefinite number of axes, which have one common center. It enables the bone to move in many places (nearly all directions).
| Ball and socket joint | |
|---|---|
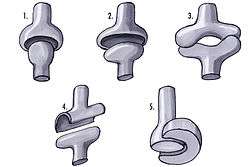 1: Ball and socket joint; 2: Condyloid joint (Ellipsoid); 3: Saddle joint; 4 Hinge joint; 5: Pivot joint; | |
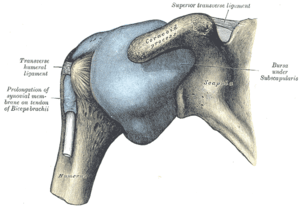 Capsule of shoulder-joint (distended). Anterior aspect. | |
| Identifiers | |
| TA | A03.0.00.050 |
| FMA | 75301 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
An enarthrosis is a special kind of spheroidal joint in which the socket covers the sphere beyond its equator.[1]
Examples
Examples of this form of articulation are found in the hip, where the round head of the femur (ball) rests in the cup-like acetabulum (socket) of the pelvis; and in the shoulder joint, where the rounded upper extremity of the humerus (ball) rests in the cup-like glenoid fossa (socket) of the shoulder blade.[2] (The shoulder also includes a sternoclavicular joint.)
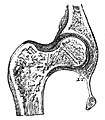 Hip
Hip Shoulder
Shoulder.svg.png) Details of hip joint.
Details of hip joint.- Femur
- Femoral Neck
- Femoral Head
- Acetabulum
- Acetabular Labrum
- Pelvis
References
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 287 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- Platzer, Werner (2008) Color Atlas of Human Anatomy, Volume 1, p.28
- And the phalanges (toes, fingers). Introduction to Joints: Synovial Joints - Ball and Socket Joints Archived 2011-07-20 at the Wayback Machine
External links