Azygos lobe
In human anatomy, an azygos lobe is a normal anatomical variation of the upper lobe of the right lung.[1] It is seen in 1% of the population. Embryologically, it arises from an anomalous lateral course of the azygos vein in a pleural septum within the apical segment of the right upper lobe or in other words an azygos lobe is formed when the right posterior cardinal vein, one of the precursors of the azygos vein, fails to migrate over the apex of the lung and penetrates it instead, carrying along two pleural layers that invaginates into the upper portion of the right upper lobe . As it has no bronchi, veins and arteries of its own or corresponding alteration in the segmental architecture of the lung, so it is not a true (misnomer), or even accessory, pulmonary lobe, but rather an anatomically separated part of the upper lobe. It is usually an incidental finding on chest x-ray or computed tomography and is as such not associated with any morbidity but can cause technical problems in thoracoscopic procedures .
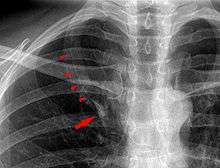
Additional images
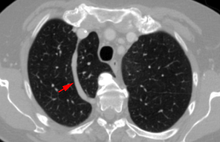
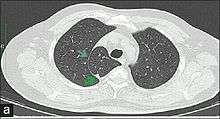
References
- Amini, Behrang. "Azygos lobe | Radiology Reference Article | Radiopaedia.org". Radiopaedia.
Further reading
- Sidhu R, Dhanadia A, Shah H, Chudasama N (May 2015). "Eluding normal variant". Lung India. 32 (3): 298–91. doi:10.4103/0970-2113.156258. PMC 4429398. PMID 25983422.
- Mata J, Cáceres J, Alegret X, Coscojuela P, De Marcos JA (May 1991). "Imaging of the azygos lobe: normal anatomy and variations" (PDF). AJR Am J Roentgenol. 156 (5): 931–7. doi:10.2214/ajr.156.5.2017954. PMID 2017954.
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Human anatomy, azygos lobe. |