Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease
Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) is the most prevalent, potentially lethal, monogenic human disorder.[1] It is associated with large interfamilial and intrafamilial variability, which can be explained to a large extent by its genetic heterogeneity and modifier genes.[1] It is also the most common of the inherited cystic kidney diseases — a group of disorders with related but distinct pathogenesis, characterized by the development of renal cysts and various extrarenal manifestations, which in case of ADPKD include cysts in other organs, such as the liver, seminal vesicles, pancreas, and arachnoid membrane, as well as other abnormalities, such as intracranial aneurysms and dolichoectasias, aortic root dilatation and aneurysms, mitral valve prolapse, and abdominal wall hernias.[1][2][3] Over 50% of patients with ADPKD eventually develop end stage kidney disease and require dialysis or kidney transplantation.[1][4] ADPKD is estimated to affect at least one in every 1000 individuals worldwide, making this disease the most common inherited kidney disorder with a diagnosed prevalence of 1:2000 and incidence of 1:3000-1:8000 in a global scale.[5][6][7][8][9]
| Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Autosomal dominant PKD, adult-onset PKD |
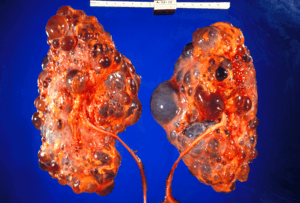 | |
| Polycystic kidneys | |
| Specialty | Medical genetics |
Signs and symptoms
- Acute loin pain
- Haematuria
- Ballotable kidneys
- Subarachnoid hemorrhage (berry aneurysm)
- Hypertension
- Associated liver cyst
- Uremia due to renal failure
- Anemia due to CKD
- Increase RBC or erythropoietin secretion
Genetics
ADPKD is genetically heterogeneous with two genes identified: PKD1 (chromosome region 16p13.3; around 85% cases) and PKD2 (4q21; around 15% cases).[1] Several genetic mechanisms probably contribute to the phenotypic expression of the disease.[1] Although evidence exists for a two-hit mechanism (germline and somatic inactivation of two PKD alleles) explaining the focal development of renal and hepatic cysts,[10][11] haploinsufficiency is more likely to account for the vascular manifestations of the disease.[12][13] Additionally, new mouse models homozygous for PKD1 hypomorphic alleles 22 and 23 and the demonstration of increased renal epithelial cell proliferation in PKD2 +/− mice suggest that mechanisms other than the two-hit hypothesis also contribute to the cystic phenotype.[1]
Large interfamilial and intrafamilial variability occurs in ADPKD.[1] Most individuals with PKD1 mutations have renal failure by age 70 years, whereas more than 50% of individuals with PKD2 mutations have adequate renal function at that age (mean age of onset of end-stage renal disease: 54·3 years with PKD1; 74·0 years with PKD2).[14]
The significant intrafamilial variability observed in the severity of renal and extrarenal manifestations points to genetic and environmental modifying factors that may influence the outcome of ADPKD, and results of an analysis of the variability in renal function between monozygotic twins and siblings support the role of genetic modifiers in this disease.[1][15] It is estimated that 43–78% of the variance in age to ESRD could be due to heritable modifying factors,[16][17] with parents as likely as children to show more severe disease in studies of parent-child pairs.[1][18]
Pathophysiology
In many patients with ADPKD, kidney dysfunction is not clinically apparent until 40 or 50 years of life.[4] However, an increasing body of evidence suggests the formation of renal cysts starts in utero.[19] Cysts initially form as small dilations in renal tubules, which then expand to form fluid-filled cavities of different sizes.[19] Factors suggested to lead to cystogenesis include a germline mutation in one of the polycystin gene alleles, a somatic second hit that leads to the loss of the normal allele, and a third hit, which can be anything that triggers cell proliferation, leading to the dilation of the tubules.[19] In the progression of the disease, continued dilation of the tubules through increased cell proliferation, fluid secretion, and separation from the parental tubule lead to the formation of cysts.[20][21]
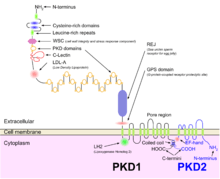
ADPKD, together with many other diseases that present with renal cysts, can be classified into a family of diseases known as ciliopathies.[22] Epithelial cells of the renal tubules, including all the segments of the nephron and the collecting ducts (with the exception of intercalated cells) show the presence of a single primary apical cilium.[23] Polycystin-1, the protein encoded by the PKD1 gene, is present on these cilia and is thought to sense the flow with its large extracellular domains, activating the calcium channels associated with polycystin-2, the product of gene PKD2,[24] as a result of the genetic setting of ADPKD as explained in the genetics sub-section above.
Epithelial cell proliferation and fluid secretion that lead to cystogenesis are two hallmark features in ADPKD.[25] During the early stages of cystogenesis, cysts are attached to their parental renal tubules and a derivative of the glomerular filtrate enters the cysts.[19] Once these cysts expand to approximately 2 mm in diameter, the cyst closes off from its parental tubule and after that fluid can only enter the cysts through transepithelial secretion, which in turn is suggested to increase due to secondary effects from an increased intracellular concentrations of cyclic AMP (cAMP).[19]
Clinically, the insidious increase in the number and size of renal cysts translates as a progressive increment in kidney volume.[1][19] Studies led by Mayo Clinic professionals established that the total kidney volume (TKV) in a large cohort of ADPKD patients was 1060 ± 642ml with a mean increase of 204ml over three years, or 5.27% per year in the natural course of the disease, among other important, novel findings that were extensively studied for the first time.[26]
Diagnosis
Usually, the diagnosis of ADPKD is initially performed by renal imaging using ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI.[27] However, molecular diagnostics can be necessary in the following situations: 1- when a definite diagnosis is required in young individuals, such as a potential living related donor in an affected family with equivocal imaging data;[27] 2- in patients with a negative family history of ADPKD, because of potential phenotypic overlap with several other kidney cystic diseases;[27] 3- in families affected by early-onset polycystic kidney disease, since in this cases hypomorphic alleles and/or oligogenic inheritance can be involved;[27][28] and 4- in patients requesting genetic counseling, especially in couples wishing a pre-implantation genetic diagnosis.[27][29]
The findings of large echogenic kidneys without distinct macroscopic cysts in an infant/child at 50% risk for ADPKD are diagnostic. In the absence of a family history of ADPKD, the presence of bilateral renal enlargement and cysts, with or without the presence of hepatic cysts, and the absence of other manifestations suggestive of a different renal cystic disease provide presumptive, but not definite, evidence for the diagnosis. In some cases, intracranial aneurysms can be an associated sign of ADPKD, and screening can be recommended for patients with a family history of intracranial aneurysm.[30]
Molecular genetic testing by linkage analysis or direct mutation screening is clinically available; however, genetic heterogeneity is a significant complication to molecular genetic testing. Sometimes, a relatively large number of affected family members need to be tested in order to establish which one of the two possible genes is responsible within each family. The large size and complexity of PKD1 and PKD2 genes, as well as marked allelic heterogeneity, present obstacles to molecular testing by direct DNA analysis. The sensitivity of testing is nearly 100% for all patients with ADPKD who are age 30 years or older and for younger patients with PKD1 mutations; these criteria are only 67% sensitive for patients with PKD2 mutations]] who are younger than age 30 years.
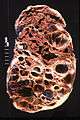 Adult polycystic kidney
Adult polycystic kidney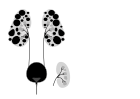 Diagram of autosomal dominant polycystic disease with a normal kidney inset for comparison
Diagram of autosomal dominant polycystic disease with a normal kidney inset for comparison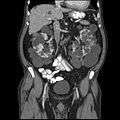 Abdominal CT scan of an adult with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease: Extensive cyst formation is seen over both kidneys, with a few cysts in the liver, as well. (Coronal plane)
Abdominal CT scan of an adult with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease: Extensive cyst formation is seen over both kidneys, with a few cysts in the liver, as well. (Coronal plane)
Treatment
Currently, the only clinical/pharmacological treatment available for ADPKD consists in reducing the speed in gain of total kidney volume (TKV) with aquaretics (i.e. tolvaptan), which can alleviate pain while giving the patients a better quality of life for over a mean of 3 years. After this period, patients can restart gaining TKV at pretreatment rates and may eventually have to go through dialysis and kidney transplant. Palliative treatment modalities involve symptomatic medications (nonopioid and opioid analgesics) for abdominal/retroperitoneal pain. Before the advent of aquaretic medication, the only option for analgesic-resistant pain was simple or complex surgical procedures (i.e. renal cyst aspiration, cyst decortication, renal denervation and nephrectomy), which can result in complications inherent to surgery.
Aquaretic medication
In 2014, Japan was the first country in the world to approve a pharmacological treatment for ADPKD[26] followed by Canada and Europe, which approved the drug tolvaptan for ADPKD patients in the beginning of 2015. The USA FDA approved the use of tolvaptan in the treatment of ADPKD in 2018.[31] Tolvaptan, an aquaretic drug, is a vasopressin receptor 2 (V2) antagonist.[8] Pre-clinical studies had suggested that the molecule cAMP could be involved in the enlargement of ADPKD cysts,[32] and studies on rodents confirmed the role of vasopressin in increasing the levels of cAMP in the kidney, which laid the basis for the conduction of clinical studies.[33] Because data from the Consortium for Radiologic Imaging Studies of Polycystic Kidney Disease (CRISP) led by Mayo Clinic showed that total kidney volume (TKV) predicted the risk of developing chronic kidney disease in patients with ADPKD,[26][34] the TEMPO 3:4 trial, which enrolled patients from 129 sites worldwide from 2007 to 2009, evaluated TKV as a primary end-point to test the efficacy of tolvaptan in ADPKD patients.[8][9] That study showed a significant decrease in the ratio of TKV increase and deterring of renal function decline in ADPKD patients after treatment with tolvaptan;[8][35] however, because laboratory test results regarding liver function appeared elevated in a percentage of patients enrolled in that study, the approval of the drug was either delayed by regulatory agencies or, as in case of the US, altogether denied.[9][36]
Analgesic medication
Chronic pain in patients with ADPKD is often refractory to conservative, noninvasive treatments, but nonopioid analgesics and conservative interventions can be first used before opioid analgesics are considered; if pain continues, then surgical interventions can target renal or hepatic cysts to directly address the cause of pain, with surgical options including renal cyst decortication, renal denervation, and nephrectomy.[37]
Renal cyst aspiration
Aspiration with ethanol sclerotherapy can be performed for the treatment of symptomatic simple renal cysts, but can be impractical in advanced patients with multiple cysts.[38] The procedure itself consists in the percutaneous insertion of a needle into the identified cyst, under ultrasound guidance, with subsequent draining the contained liquid; the sclerotherapy is used to avoid liquid reaccumulation that can occur in the cyst, which can result in symptom recurrence.[38][39]
Laparoscopic cyst decortication
Laparoscopic cyst decortication (also referred to as marsupialization) consists in the removal of one or more kidney cysts through laparoscopic surgery, during which cysts are punctured, and the outer wall of the larger cysts is excised with care not to incise the renal parenchyma.[40][41] This procedure can be useful for pain relief in patients with ADPKD, and is usually indicated after earlier cyst aspiration has confirmed that the cyst to be decorticated is responsible for pain.[41] Nonrandomised controlled trials conducted in the '90s showed that patients with symptomatic simple renal cysts who had recurrence of symptoms after initial response to simple aspiration could be safely submitted to cyst decortication, with a mean pain-free life between 17 and 24 months after surgery.[40][42] Laparoscopic decortication presents a 5% recurrence rate of renal cysts compared to an 82% recurrence rate obtained with sclerotherapy.[39]
Neurolysis
A novel treatment of specifically the chronic pain suffered by many sufferers of ADPKD is Celiac plexus neurolysis.[43][44] This involves the chemical ablation of the celiac plexus, to cause a temporary degeneration of targeted nerve fibers. When the nerve fibers degenerate, it causes an interruption in the transmission of nerve signals. This treatment, when successful, provides significant pain relief for a period ranging from a few days to over a year. The procedure may be repeated when the affected nerves have healed and the pain returns.
Nephrectomy
Many ADPKD patients suffer symptomatic sequelae in consequence of the disease, such as cyst hemorrhage, flank pain, recurrent infections, nephrolithiasis, and symptoms of mass effect (i.e., early satiety, nausea and vomiting, and abdominal discomfort), from their enlarged kidneys.[45][46][47] In such cases, nephrectomy can be required due to intractable symptoms or when in the course of preparing for kidney transplantation, the native kidneys are found to impinge upon the true pelvis and preclude the placement of a donor allograft.[46][47][48][49] Additionally, native nephrectomy may be undertaken in the presence of suspected malignancy, as renal cell carcinoma (RCC) is two to three times more likely in the ADPKD population in end-stage kidney disease (ESKD) than in the ESKD patients without ADPKD.[47][50] Although the indications for nephrectomy in ADPKD may be related to kidney size, the decision to proceed with native nephrectomy is often undertaken on an individual basis, without specific reference to kidney size measurements.[47]
Dialysis
Two modalities of dialysis can be used in the treatment of ADPKD patients: peritoneal dialysis and hemodialysis.[51] Epidemiological data shows that ADPKD affects 5-13.4% of patients undergoing hemodialysis in Europe and in the United States,[52][53][54] and about 3% in Japan.[55] Peritoneal dialysis has usually been contra-indicated in ADPKD patients with large kidney and liver volumes, due to expected physical difficulties in the procedure and possible complications;[51][56] however, no difference is seen in long-term morbidity between hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis in ADPKD.[51]
Kidney transplant
Kidney transplantation is accepted as the preferred treatment for ADPKD patients with ESRD.[1] Among American patients on the kidney-transplant waiting list (as of December 2011), 7256 (8.4%) were listed due to cystic kidney disease and of the 16,055 renal transplants performed in 2011, 2057 (12.8%) were done for patients with cystic kidney disease, with 1,189 from deceased donors and 868 from living donors.[57]
Prognosis
In ADPKD patients, gradual cyst development and expansion result in kidney enlargement, and during the course of the disease, glomerular filtration rate remains normal for decades before kidney function starts to progressively deteriorate, making early prediction of renal outcome difficult.[58] The CRISP study,[26][34] mentioned in the treatment section above, contributed to build a strong rationale supporting the prognostic value of total kidney volume (TKV) in ADPKD; TKV (evaluated by MRI) increases steadily and a higher rate of kidney enlargement correlated with accelerated decline of GFR, while patient height-adjusted TKV (HtTKV) ≥600 ml/m predicts the development of stage 3 chronic kidney disease within 8 years.[58]
Besides TKV and HtTKV, the estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) has also been tentatively used to predict the progression of ADPKD.[58] After the analysis of CT or MRI scans of 590 patients with ADPKD treated at the Mayo Translational Polycystic Kidney Disease Center, Irazabal and colleagues developed an imaging-based classification system to predict the rate of eGFR decline in patients with ADPKD.[58][59] In this prognostic method, patients are divided into five subclasses of estimated kidney growth rates according to age-specific HtTKV ranges (1A, <1.5%; 1B, 1.5–3.0%; 1C, 3.0–4.5%; 1D, 4.5–6.0%; and 1E, >6.0%) as delineated in the CRISP study.[58][59] The decline in eGFR over the years following initial TKV measurement is significantly different between all five patient subclasses, with those in subclass 1E having the most rapid decline.[58] Some of the most common causes of death in patients with ADPKD are various infections (25%), a ruptured berry aneurysm (15%), or coronary/hypertensive heart disease (40%).[60]
References
- Torres VE, Harris PC, Pirson Y (2007). "Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease". Lancet. 369 (9569): 1287–1301. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(07)60601-1. PMID 17434405.
- Dalgaard OZ (1957). "Bilateral polycystic disease of the kidneys; a follow-up of two hundred and eighty-four patients and their families". Acta Med. Scand. Suppl. 328: 1–255. PMID 13469269.
- Torres, Vicente; Harris, Peter C (20 May 2009). "Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease: the last 3 years". Kidney International. 76 (2): 149–168. doi:10.1038/ki.2009.128. PMC 2812475. PMID 19455193.
- Grantham JJ (2008). "Clinical practice. Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease". N. Engl. J. Med. 359 (14): 1477–1485. doi:10.1056/NEJMcp0804458. PMID 18832246.; Reprinted in Niemczyk M, Niemczyk S, Paczek L (2009). "Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease and transplantation". Ann Transplant. 14 (4): 86–90. PMC 2843931. PMID 20009161.
- Muto S, Kawano H, Higashihara E, Narita I, Ubara Y, Matsuzaki T, Ouyang J, Torres VE, Horie S (2015). "The effect of tolvaptan on autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease patients: a subgroup analysis of the Japanese patient subset from TEMPO 3:4 trial". Clin Exp Nephrol. 19 (5): 867–877. doi:10.1007/s10157-015-1086-2. PMID 25663351.
- Higashihara E, Nutahara K, Kojima M, Tamakoshi A, Yoshiyuki O, Sakai H, Kurokawa K (1998). "Prevalence and renal prognosis of diagnosed autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease in Japan". Nephron. 80 (4): 421–427. doi:10.1159/000045214. PMID 9832641.
- Levy M, Feingold J (2000). "Estimating prevalence in single-gene kidney diseases progressing to renal failure". Kidney Int. 58 (3): 925–943. doi:10.1046/j.1523-1755.2000.00250.x. PMID 10972657.
- Torres VE, Chapman AB, Devuyst O, Gansevoort RT, Grantham JJ, Higashihara E, Perrone RD, Krasa HB, Ouyang J, Czerwiec FS (2012). "Tolvaptan in patients with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease". N. Engl. J. Med. 367 (25): 2407–2418. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1205511. PMC 3760207. PMID 23121377.
- Cornec-Le Gall E, Le Meur Y (2014). "Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease: is the treatment for tomorrow?". Nephrol. Ther. 10 (6): 433–440. doi:10.1016/j.nephro.2014.03.003. PMID 25086476.
- Torra R, Badenas C, San Millán JL, Pérez-Oller L, Estivill X, Darnell A (1999). "A loss-of-function model for cystogenesis in human autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease type 2". Am. J. Hum. Genet. 65 (2): 345–352. doi:10.1086/302501. PMC 1377933. PMID 10417277.
- Watnick TJ, Torres VE, Gandolph MA, Qian F, Onuchic LF, Klinger KW, Landes G, Germino GG (1998). "Somatic mutation in individual liver cysts supports a two-hit model of cystogenesis in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease". Mol. Cell. 2 (2): 247–251. doi:10.1016/s1097-2765(00)80135-5. PMID 9734362.
- Qian Q, Hunter LW, Li M, Marin-Padilla M, Prakash YS, Somlo S, Harris PC, Torres VE, Sieck GC (2003). "PKD2 haploinsufficiency alters intracellular calcium regulation in vascular smooth muscle cells". Mol. Cell. 12 (15): 1875–1880. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddg190. PMID 12874107.
- Gao Z, Joseph E, Ruden DM, Lu X (2004). "Drosophila Pkd2 is haploid-insufficient for mediating optimal smooth muscle contractility". J. Biol. Chem. 279 (14): 14225–14231. doi:10.1074/jbc.M312223200. PMID 14732716.
- Hateboer N, v Dijk MA, Bogdanova N, Coto E, Saggar-Malik AK, San Millan JL, Torra R, Breuning M, Ravine D (1999). "Comparison of phenotypes of polycystic kidney disease types 1 and 2. European PKD1-PKD2 Study Group". Lancet. 353 (9147): 103–107. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(98)03495-3. PMID 10023895.
- Persu A, Duyme M, Pirson Y, Lens XM, Messiaen T, Breuning MH, Chauveau D, Levy M, Grünfeld JP, Devuyst O (2004). "Comparison between siblings and twins supports a role for modifier genes in ADPKD". Kidney Int. 66 (6): 2132–2136. doi:10.1111/j.1523-1755.2004.66003.x. PMID 15569302.
- Fain PR, McFann KK, Taylor MR, Tison M, Johnson AM, Reed B, Schrier RW (2005). "Modifier genes play a significant role in the phenotypic expression of PKD1". Kidney Int. 67 (4): 1256–1267. doi:10.1111/j.1523-1755.2005.00203.x. PMID 15780078.
- Paterson AD, Magistroni R, He N, Wang K, Johnson A, Fain PR, Dicks E, Parfrey P, St George-Hyslop P, Pei Y (2005). "Progressive loss of renal function is an age-dependent heritable trait in type 1 autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease". J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 16 (3): 755–762. doi:10.1681/ASN.2004090758. PMID 15677307.
- Geberth S, Ritz E, Zeier M, Stier E (1995). "Anticipation of age at renal death in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD)?". Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 10 (9): 1603–1606. PMID 8559477.
- Paul BM, Vanden Heuvel GB (2014). "Kidney: polycystic kidney disease". Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Dev. Biol. 3 (6): 465–487. doi:10.1002/wdev.152. PMC 4423807. PMID 25186187.
- Igarashi P, Somlo S (2002). "Genetics and pathogenesis of polycystic kidney disease". J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 13 (9): 2384–2398. doi:10.1097/01.asn.0000028643.17901.42. PMID 12191984.
- Parnell SC, Magenheimer BS, Maser RL, Zien CA, Frischauf AM, Calvet JP (2002). "Polycystin-1 activation of c-Jun N-terminal kinase and AP-1 is mediated by heterotrimeric G proteins". J. Biol. Chem. 277 (22): 19566–19572. doi:10.1074/jbc.M201875200. PMID 11912216.
- Berbari NF, O'Connor AK, Haycraft CJ, Yoder BK (2009). "The primary cilium as a complex signaling center". Curr. Biol. 19 (13): R526–R535. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2009.05.025. PMC 2814769. PMID 19602418.
- Reed BY, McFann K, Bekheirnia MR, Nobakhthaghighi N, Masoumi A, Johnson AM, Shamshirsaz AA, Kelleher CL, Schrier RW (2008). "Variation in age at ESRD in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease". Am. J. Kidney Dis. 51 (2): 173–183. doi:10.1053/j.ajkd.2007.10.037. PMC 2747334. PMID 18215695.
- Chapin HC, Caplan MJ (2010). "The cell biology of polycystic kidney disease". J. Cell Biol. 191 (4): 701–710. doi:10.1083/jcb.201006173. PMC 2983067. PMID 21079243.
- Belibi FA, Reif G, Wallace DP, Yamaguchi T, Olsen L, Li H, Helmkamp GM, Grantham JJ (2004). "Cyclic AMP promotes growth and secretion in human polycystic kidney epithelial cells". Kidney Int. 66 (3): 964–973. doi:10.1111/j.1523-1755.2004.00843.x. PMID 15327388.
- Torres VE (2010). "Treatment strategies and clinical trial design in ADPKD". Adv. Chronic Kidney Dis. 17 (2): 190–204. doi:10.1053/j.ackd.2010.01.006. PMC 4127876. PMID 20219622.
- Trujillano D, Bullich G, Ossowski S, Ballarín J, Torra R, Estivill X, Ars E (2014). "Diagnosis of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease using efficient PKD1 and PKD2 targeted next-generation sequencing". Mol. Genet. Genomic Med. 2 (5): 412–421. doi:10.1002/mgg3.82. PMC 4190876. PMID 25333066.
- Bergmann C, von Bothmer J, Ortiz Brüchle N, Venghaus A, Frank V, Fehrenbach H, Hampel T, Pape L, Buske A, Jonsson J, Sarioglu N, Santos A, Ferreira JC, Becker JU, Cremer R, Hoefele J, Benz MR, Weber LT, Buettner R, Zerres K (2011). "Mutations in multiple PKD genes may explain early and severe polycystic kidney disease". J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 22 (11): 2047–2056. doi:10.1681/ASN.2010101080. PMC 3279997. PMID 22034641.
- Harris PC, Rossetti S (2010). "Molecular diagnostics for autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease". Nature Reviews Nephrology. 6 (4): 197–206. doi:10.1038/nrneph.2010.18. PMC 4050432. PMID 20177400.
- Rozenfeld MN, Ansari SA, Shaibani A, Russell EJ, Mohan P, Hurley MC (2013). "Should patients with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease be screened for cerebral aneurysms?" (PDF). AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 35 (1): 3–9. doi:10.3174/ajnr.A3437. PMID 23292526.
- "Tolvaptan Cleared in US for ADPKD in Adults". 2018-04-26.
- Hanaoka K, Guggino WB (2000). "cAMP regulates cell proliferation and cyst formation in autosomal polycystic kidney disease cells". J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 11 (7): 1179–1187. PMID 10864573.
- Juul KV, Bichet DG, Nielsen S, Nørgaard JP (2014). "The physiological and pathophysiological functions of renal and extrarenal vasopressin V2 receptors". Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 306 (9): F931–940. doi:10.1152/ajprenal.00604.2013. PMID 24598801.
- Irazabal MV, Rangel LJ, Bergstralh EJ, Osborn SL, Harmon AJ, Sundsbak JL, Bae KT, Chapman AB, Grantham JJ, Mrug M, Hogan MC, El-Zoghby ZM, Harris PC, Erickson BJ, King BF, Torres VE (2015). "Imaging classification of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease: a simple model for selecting patients for clinical trials". J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 26 (1): 160–172. doi:10.1681/ASN.2013101138. PMC 4279733. PMID 24904092.
- Kelsey R (2013). "Tolvaptan in ADPKD – TEMPO 3:4 trial results". Nature Reviews Nephrology. 9 (1): 1. doi:10.1038/nrneph.2012.236. PMID 23183839.
- Brown T (2013). "Tolvaptan Not Recommended for ADPKD". Medscape.
- Tellman MW, Bahler CD, Shumate AM, Bacallao RL, Sundaram CP (2015). "Management of Pain in ADPKD and Anatomy of Renal Innervation". J. Urol. 193 (5): 1470–1478. doi:10.1016/j.juro.2014.10.124. hdl:1805/7798. PMID 25534330.
- Mohsen T, Gomha MA (2005). "Treatment of symptomatic simple renal cysts by percutaneous aspiration and ethanol sclerotherapy". BJU Int. 96 (9): 1369–1372. doi:10.1111/j.1464-410X.2005.05851.x. PMID 16287460.
- Okeke AA, Mitchelmore AE, Keeley FX, Timoney AG (2003). "A comparison of aspiration and sclerotherapy with laparoscopic de-roofing in the management of symptomatic simple renal cysts". BJU Int. 92 (6): 610–613. doi:10.1046/j.1464-410x.2003.04417.x. PMID 14511045.
- Brown JA, Torres VE, King BF, Segura JW (1996). "Laparoscopic marsupialization of symptomatic polycystic kidney disease". J. Urol. 156 (1): 22–27. doi:10.1016/s0022-5347(01)65927-5. PMID 8648810.
- McDougall EM (2000). "Approach to decortication of simple cysts and polycystic kidneys". J Endourol. 14 (10): 821–827. doi:10.1089/end.2000.14.821. PMID 11206615.
- Consonni P, Nava L, Scattoni V, Bianchi A, Spaliviero M, Guazzoni G, Bellinzoni P, Bocciardi A, Rigatti P (1996). "Percutaneous echo-guided drainage and sclerotherapy of symptomatic renal cysts: critical comparison with laparoscopic treatment". Arch. Ital. Urol. Androl. 68 (5 Suppl): 27–30. PMID 9162369.
- https://www.nierstichting.nl/media/filer_public/ae/78/ae7818bc-0593-4c55-9357-5e7c24bb375a/2017-kidneyinternational-casteleijn-nerve_blocks_for_pain_in_adpkd.pdf
- Nitschke, A. M; Ray Jr, C. E (2013). "Percutaneous Neurolytic Celiac Plexus Block". Seminars in Interventional Radiology. 30 (3): 318–321. doi:10.1055/s-0033-1353485. PMC 3773031. PMID 24436554.
- Alam A, Perrone RD (2010). "Management of ESRD in patients with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease". Adv. Chronic Kidney Dis. 17 (2): 164–172. doi:10.1053/j.ackd.2009.12.006. PMID 20219619.
- Wagner MD, Prather JC, Barry JM (2007). "Selective, concurrent bilateral nephrectomies at renal transplantation for autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease". J. Urol. 177 (6): 2250–2254. doi:10.1016/j.juro.2007.01.146. PMID 17509331.
- Cristea O, Yanko D, Felbel S, House A, Sener A, Luke PP (2014). "Maximal kidney length predicts need for native nephrectomy in ADPKD patients undergoing renal transplantation". Can. Urol. Assoc. J. 8 (7–8): 278–282. doi:10.5489/cuaj.2128. PMC 4137014. PMID 25210553.
- Fuller TF, Brennan TV, Feng S, Kang SM, Stock PG, Freise CE (2005). "End stage polycystic kidney disease: indications and timing of native nephrectomy relative to kidney transplantation". J. Urol. 174 (6): 2284–2288. doi:10.1097/01.ju.0000181208.06507.aa. PMID 16280813.
- Cohen D, Timsit MO, Chrétien Y, Thiounn N, Vassiliu V, Mamzer MF, Legendre C, Méjean A (2008). "Place of nephrectomy in patients with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease waiting for renal transplantation". Prog. Urol. 18 (10): 642–649. doi:10.1016/j.purol.2008.06.004. PMID 18971106.
- Hajj P, Ferlicot S, Massoud W, Awad A, Hammoudi Y, Charpentier B, Durrbach A, Droupy S, Benoît G (2009). "Prevalence of renal cell carcinoma in patients with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease and chronic renal failure". Urology. 74 (3): 631–634. doi:10.1016/j.urology.2009.02.078. PMID 19616833.
- Courivaud C, Roubiou C, Delabrousse E, Bresson-Vautrin C, Chalopin JM, Ducloux D (2014). "Polycystic kidney size and outcomes on peritoneal dialysis: comparison with haemodialysis". Clin Kidney J. 7 (2): 138–143. doi:10.1093/ckj/sft171. PMC 4377775. PMID 25852862.
- Nunes AC, Milani V, Porsch DB, Rossato LB, Mattos CB, Roisenberg I, Barros EJ (2008). "Frequency and clinical profile of patients with polycystic kidney disease in southern Brazil". Ren. Fail. 30 (2): 169–173. doi:10.1080/08860220701810265. PMID 18300116.
- Bleyer AJ, Hart TC (2004). "Polycystic kidney disease" (PDF). N. Engl. J. Med. 350 (25): 2622. doi:10.1056/NEJM200406173502519. PMID 15201424.
- Corradi V, Gastaldon F, Virzì GM, de Cal M, Soni S, Chionh C, Cruz DN, Clementi M, Ronco C (2009). "Clinical pattern of adult polycystic kidney disease in a northeastern region of Italy". Clin. Nephrol. 72 (4): 259–267. doi:10.5414/CNP72259. PMID 19825331.
- Higashihara E, Nutahara K, Kojima M, Tamakoshi A, Yoshiyuki O, Sakai H, Kurokawa K (1998). "Prevalence and renal prognosis of diagnosed autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease in Japan". Nephron. 80 (4): 421–427. doi:10.1159/000045214. PMID 9832641.
- Hamanoue S, Hoshino J, Suwabe T, Marui Y, Ueno T, Kikuchi K, Hazue R, Mise K, Kawada M, Imafuku A, Hayami N, Sumida K, Hiramatsu R, Hasegawa E, Sawa N, Takaichi K, Ubara Y (2015). "Peritoneal Dialysis is Limited by Kidney and Liver Volume in Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease". Ther. Apher. Dial. 19 (3): 207–11. doi:10.1111/1744-9987.12272. PMID 25612237.
- Matas AJ, Smith JM, Skeans MA, Lamb KE, Gustafson SK, Samana CJ, Stewart DE, Snyder JJ, Israni AK, Kasiske BL (2013). "OPTN/SRTR 2011 Annual Data Report: kidney". Am. J. Transplant. 13 (Suppl 1): 11–46. doi:10.1111/ajt.12019. PMC 5527691. PMID 23237695.
- Cornec-Le Gall E, Le Meur Y (2014). "Polycystic kidney disease: Kidney volume--a crystal ball for ADPKD prognosis?". Nature Reviews Nephrology. 10 (9): 485–486. doi:10.1038/nrneph.2014.132. PMID 25092148.
- Irazabal MV, Rangel LJ, Bergstralh EJ, Osborn SL, Harmon AJ, Sundsbak JL, Bae KT, Chapman AB, Grantham JJ, Mrug M, Hogan MC, El-Zoghby ZM, Harris PC, Erickson BJ, King BF, Torres VE (2015). "Imaging classification of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease: a simple model for selecting patients for clinical trials". J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 26 (1): 160–172. doi:10.1681/ASN.2013101138. PMC 4279733. PMID 24904092.
- Kumar, Vinay; Abbas, Abul K.; Aster, Jon C. (2014). Robbins and Cotran pathologic basis of disease. Kumar, Vinay, 1944-, Abbas, Abul K.,, Aster, Jon C.,, Perkins, James A. (Ninth ed.). Philadelphia, PA. p. 947. ISBN 9781455726134. OCLC 879416939.
External links
| Classification | |
|---|---|
| External resources |
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. |