Alveolar gland
If glands are categorized by shape, alveolar glands contrast with tubular glands. Alveolar glands have a saclike secretory portion, and are also termed saccular glands. They typically have an enlarged lumen (cavity), hence the name similar to alveoli, the very small air sacs in the lungs.
| Alveolar gland | |
|---|---|
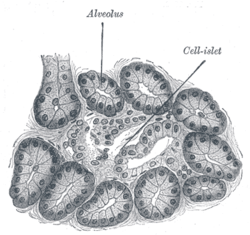 Section of pancreas of dog. X 250. | |
| Identifiers | |
| TH | H2.00.02.0.03028 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
| Look up alveolar in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
| Look up tubuloalveolar in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
Some sources draw a clear distinction between acinar and alveolar glands, based upon the size of the lumen.[1] A further complication in the case of the alveolar glands may occur in the form of still smaller saccular diverticuli growing out from the main sacculi.
The term "racemose gland"[2] is used to describe a "compound alveolar gland" or "compound acinar gland."[3]
Branched alveolar glands are classified as follows:
| Type | Description | Location | |
|---|---|---|---|
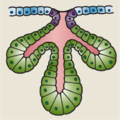 |
simple branched acinar |
thyroid glands | |
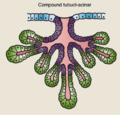 |
tubuloalveolar or tubulo-alveolar or tubulo-acinar or compound tubulo-acinar or compound tubuloalveolar[4] |
glands that start out as simple branched tubular, and branch further to terminate in alveoli | salivary glands,[5] esophagus[6] mammary glands |
Additional images
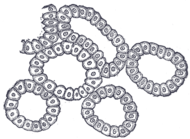 Alveoli of lacrimal gland.
Alveoli of lacrimal gland.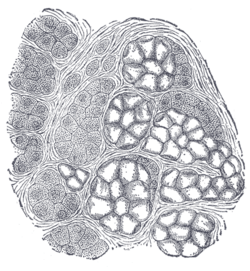 Human submaxillary gland. At the right is a group of mucous alveoli, at the left a group of serous alveoli.
Human submaxillary gland. At the right is a group of mucous alveoli, at the left a group of serous alveoli.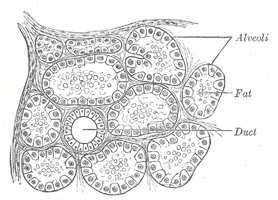 Section of portion of mamma.
Section of portion of mamma.
See also
References
- Classification of Exocrine Glands
- Racemose+gland at eMedicine Dictionary
- SIU SOM Histology GI
- Histology at KUMC glands-glands17
- Histology at KUMC glands-glands14 "Compound Tubulo- Alveolar"
- MedEd at Loyola histo/practical/epithelium/hp1-28.html
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.