Adenomatoid tumor
Adenomatoid tumor is a benign mesothelial tumor, which arises from the lining of organs. It generally presents in the genital tract, in regions such as the testis[1] and epididymis.[2] It is the second most common extratesticular scrotal mass, after lipoma, and accounts for 30% of these masses.[3] It also has been found in the pancreas.[4]
| Adenomatoid tumor | |
|---|---|
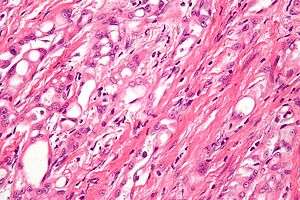 | |
| High-magnification micrograph of an adenomatoid tumor. H&E stain. | |
| Specialty | Oncology |
In the female, it has been found in the body of the uterus and the fallopian tube.[5]
Additional images
Adenomatoid tumour of the epididymis
References
- Williams SB, Han M, Jones R, Andrawis R (2004). "Adenomatoid tumor of the testes". Urology. 63 (4): 779–81. doi:10.1016/j.urology.2003.11.035. PMID 15072910.
- "Adenomatoid tumor of the epididymis". Archived from the original on 2007-06-15. Retrieved 2007-12-15.
- Cassidy, Fiona Hughes; Ishioka, Kevin M.; McMahon, Colm J.; Chu, Pauline; Sakamoto, Kyoko; Lee, Karen S.; Aganovic, Lejla (May 2010). "MR Imaging of Scrotal Tumors and Pseudotumors". RadioGraphics. 30 (3): 665–683. doi:10.1148/rg.303095049. PMID 20462987.
- Overstreet K, Wixom C, Shabaik A, Bouvet M, Herndier B (Jun 2003). "Adenomatoid tumor of the pancreas: a case report with comparison of histology and aspiration cytology". Mod. Pathol. 16 (6): 613–7. doi:10.1097/01.MP.0000072803.37527.C8. PMID 12808068.
- Huang CC, Chang DY, Chen CK, Chou YY, Huang SC (Sep 1995). "Adenomatoid tumor of the female genital tract". Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 50 (3): 275–80. doi:10.1016/0020-7292(95)02453-J. PMID 8543111.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.