16α-Hydroxyestrone
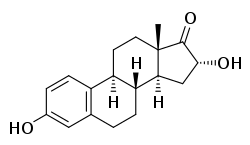
16α-Hydroxyestrone (16α-OH-E1), or hydroxyestrone, also known as estra-1,3,5(10)-triene-3,16α-diol-17-one, is an endogenous steroidal estrogen and a major metabolite of estrone, as well as an intermediate in the biosynthesis of estriol.[1][2] It is a potent estrogen similarly to estrone, and it has been suggested that the ratio of 16α-hydroxyestrone to 2-hydroxyestrone, the latter being much less estrogenic in comparison and even antiestrogenic in the presence of more potent estrogens like estradiol, may be involved in the pathophysiology of breast cancer.[1] Conversely, 16α-hydroxyestrone may help to protect against osteoporosis.[1] In contrast to estradiol, the binding of 16α-hydroxyestrone to the estrogen receptor is, uniquely, covalent and irreversible, and genotoxicity and aberrant hyperproliferations may result.[3] A diacetate ester of 16α-hydroxyestrone, hydroxyestrone diacetate, has been marketed and is used medically as an estrogen in Europe.[4][5]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(8R,9S,13S,14S,16R)-3,16-Dihydroxy-13-methyl-7,8,9,11,12,14,15,16-octahydro-6H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-one | |
| Other names
Hydroxyestrone; 16-Hydroxyestrone | |
| Identifiers | |
CAS Number |
|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.164.941 |
PubChem CID |
|
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
Chemical formula |
C18H22O3 |
| Molar mass | 286.371 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
See also
- 2-Hydroxyestrone
- 2-Hydroxyestradiol
- 16α-Hydroxydehydroepiandrosterone
- 16α-Hydroxyandrostenedione
- 15α-Hydroxydehydroepiandrosterone
References
- Rakel D (2012). Integrative Medicine. Elsevier Health Sciences. pp. 338–339. ISBN 1-4377-1793-4.
- Vitamins and Hormones. Academic Press. 7 September 2005. pp. 282–. ISBN 978-0-08-045978-3.
- Oettel M, Schillinger E (6 December 2012). Estrogens and Antiestrogens I: Physiology and Mechanisms of Action of Estrogens and Antiestrogens. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 252–. ISBN 978-3-642-58616-3.
- Index Nominum 2000: International Drug Directory. Taylor & Francis. January 2000. pp. 1250–. ISBN 978-3-88763-075-1.
- Muller NF, Dessing RP, European Society of Clinical Pharmacy (19 June 1998). European Drug Index: European Drug Registrations (Fourth ed.). CRC Press. pp. 289–. ISBN 978-3-7692-2114-5.